Task Scheduler helps you schedule automated tasks that run your programs or scripts at a specific time. Task Scheduler monitors the time and events on your computer and performs the task as soon as the criteria are satisfied. In this article, I will show you how to use Task Scheduler Windows 10.
What is Task Scheduler?
Task Scheduler is a built-in tool that allows you to schedule tasks to run automatically at a specific time, date, or event. Task Scheduler is a feature of Windows 10. The task scheduler lets you schedule commands or programs to start at various times, dates, and intervals on your computer.
How to create a task in Task Scheduler Windows 10?
The first step is to launch the Task Scheduler by opening the Start menu and typing “Task Scheduler”. Once it appears in the search results, select it.
After you launch Task Scheduler, you’ll be greeted with a window:
Now that we have our blank slate ready, let’s create a new task. To do so, click “Create Task” on the right-hand side of this window and enter a name for your task in its respective field. When you’ve chosen what name you want to use for this automated job—and made sure it’s spelled correctly—hit Next at the bottom of this window.
How to run a task on a schedule?
- Open Task Scheduler. To do this, click the Start button and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools and then click Task Scheduler.
- Create a new task from scratch by clicking Create Basic Task on the left-hand pane of the window that appears when you open Task Scheduler for the first time, which launches a wizard that walks you through creating your first scheduled task in Windows 10.
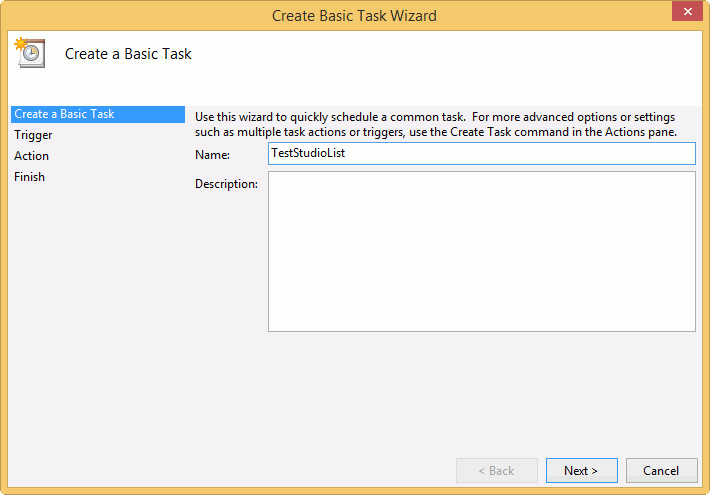
- Enter an appropriate name for this task in the Title field – name it something descriptive like “Check Email Daily” or “System Maintenance”. You can leave the Description field blank if you don’t want any description associated with your task but I recommend adding one so that it’s easy to identify later if there are multiple tasks set up on your computer at any given time.
How to use Triggers and Conditions in Task Scheduler?
You can use triggers and conditions in Task Scheduler to run a task at a specific time, or when a specific event occurs.
Here is an example of using triggers and conditions:
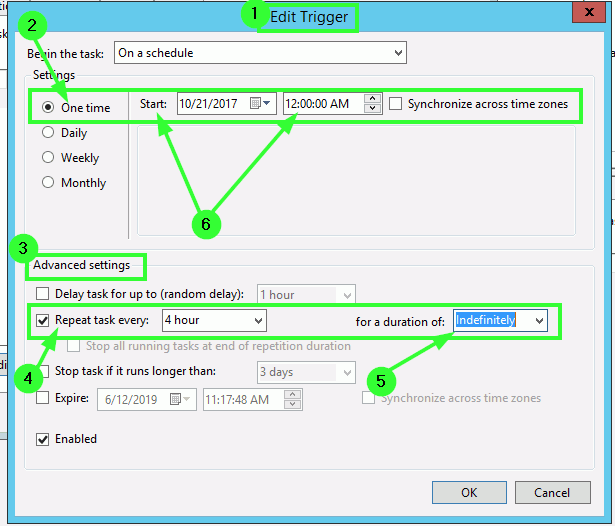
- Create a task that runs every day at 3:00 PM. This can be achieved by specifying the Start Date as Today and End Date as 1/1/0001. Unless you specify otherwise, all tasks will run from 12:00 AM to 12:00 AM.
- Create a new task that runs once a week on Monday at 9:30 a.m., but only if the system has been idle for 30 minutes before its planned start time (after 1 hour).
How to set up an action for your task?
The most commonly used action is Start Program, which allows you to run a program, batch file, or PowerShell script. To get started, go to the activities list and click “Run” and then “Run an executable” from the drop-down menu. When the task starts, you may type in any executable or script that you wish Task Scheduler to run.
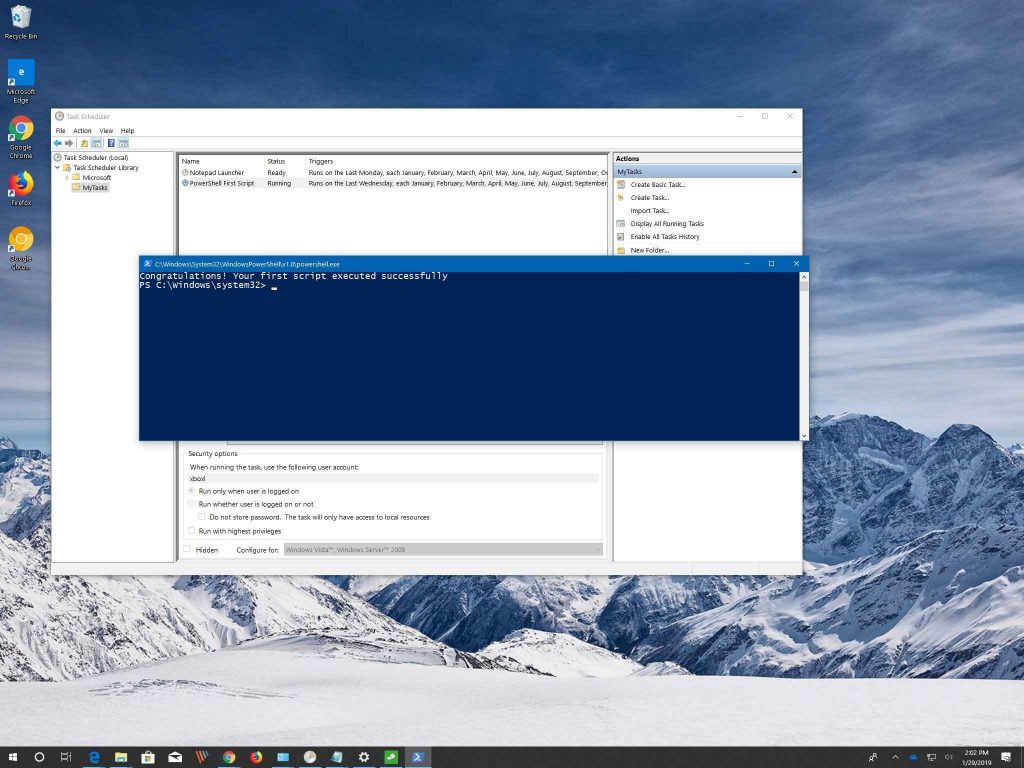
You can also use this action to start a program that doesn’t have an executable file associated with it, such as WordPad or Notepad. Simply select “Start a program” from under “Run” in your Action Settings tab and specify either cmd or PowerShell as your application type (make sure they’re both selected). Then input whatever command-line switches necessary into that window so that they work properly when executed through Task Scheduler—for example, starting them with C:\…\Wordpad \ wordpad.exe instead of just Wordpad.
How to create multiple triggers for your task?
You can create multiple triggers for your task.
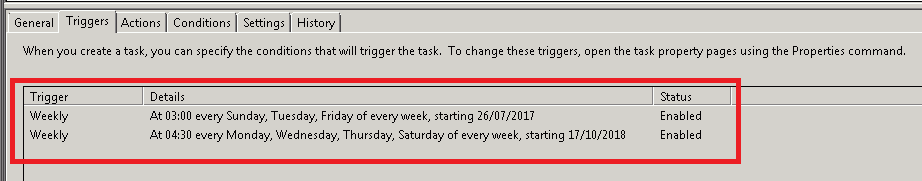
To create multiple triggers for your task, follow these steps:
- In Task Scheduler, right-click on the task you want to add a trigger to and then click Properties in the context menu that opens.
- Switch to the Triggers tab and click the New button under the Trigger section of this tab. This will open up Add Trigger dialog box where you can add one or more triggers to execute the task at regular intervals or on particular events like Logon, Logoff, Startup, etc.
How to set up conditions for your triggers in Task Scheduler?
In Task Scheduler, you may create criteria for your triggers. You can use conditions to define when a task should be executed. You may, for example, want the task to begin at a specified time or only when certain events occur.
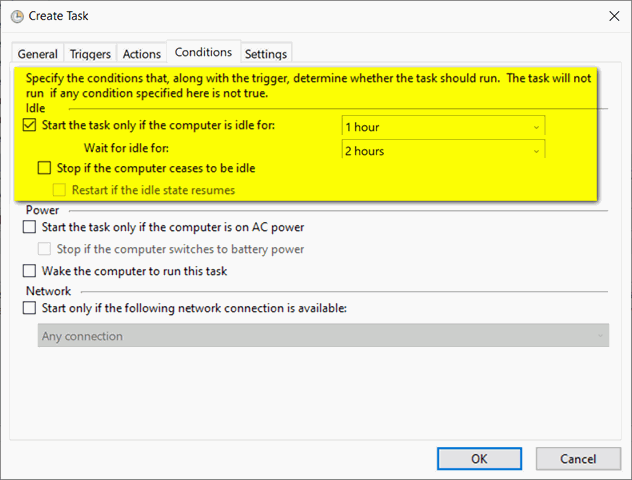
Conditions can be used to perform tasks only when particular events occur, such as the opening of an application or the creation of a file.
Should I use another tool instead of Windows 10 Task Scheduler?
If you’re using Windows 10, there’s a good chance that Task Scheduler is already built into your system. Starting with Windows 8 and continuing through to today’s latest edition of the operating system, it’s always been part of the OS. If you have an older copy of Windows installed on your computer (such as XP or Vista), then there’s still a chance that you can use Task Scheduler.
Task Scheduler has been around since Windows NT 4 back in 1996. As such, it isn’t just useful for creating automated tasks today. It also provides a great historical perspective on how we’ve automated our workflows over time.
Conclusion
Automation is one of the most helpful tools you can use to make your work more efficient. Luckily, Microsoft has built this functionality into Windows 10. Task Scheduler is the tool that lets you create automated tasks in Windows 10 and set them up to run at a particular time or when certain conditions are met. It’s easy to use once you know its features and how to access it, and it can save you hours each week if used properly.
In this blog post, I have covered everything from what Task Scheduler does for your system down to how specific triggers work within Task Scheduler itself. I hope that you enjoy learning about all of these features because they can improve your life as both a user and creator of software!



